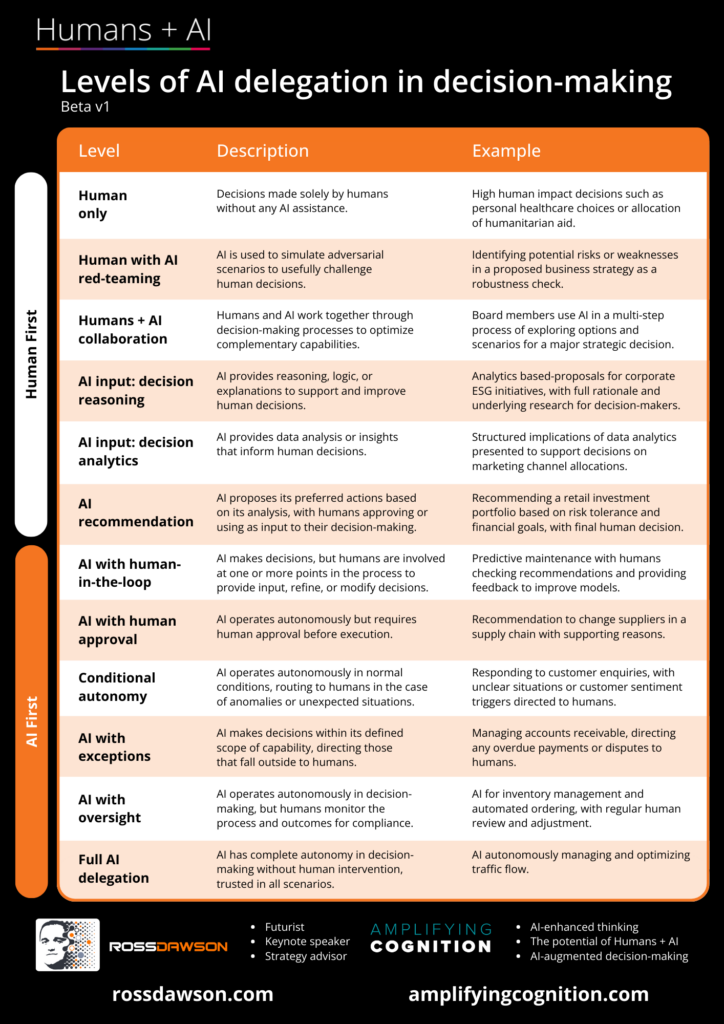
A map of levels of AI delegation in decision-making.
Click on the image for the full size pdf.
Levels of AI Delegation in Decision-Making
Beta v1
Human only
- Description: Decisions made solely by humans without any AI assistance.
- Example: High human impact decisions such as personal healthcare choices or allocation of humanitarian aid.
Human with AI red-teaming
- Description: AI is used to simulate adversarial scenarios to usefully challenge human decisions.
- Example: Identifying potential risks or weaknesses in a proposed business strategy as a robustness check.
Humans + AI collaboration
- Description: Humans and AI work together through decision-making processes to optimize complementary capabilities.
- Example: Board members use AI in a multi-step process of exploring options and scenarios for a major strategic decision.
AI input: decision reasoning
- Description: AI provides reasoning, logic, or explanations to support and improve human decisions.
- Example: Analytics-based proposals for corporate ESG initiatives, with full rationale and underlying research for decision-makers.
AI input: decision analytics
- Description: AI provides data analysis or insights that inform human decisions.
- Example: Structured implications of data analytics presented to support decisions on marketing channel allocations.
AI recommendation
- Description: AI proposes its preferred actions based on its analysis, with humans approving or using as input to their decision-making.
- Example: Recommending a retail investment portfolio based on risk tolerance and financial goals, with final human decision.
AI with human-in-the-loop
- Description: AI makes decisions, but humans are involved at one or more points in the process to provide input, refine, or modify decisions.
- Example: Predictive maintenance with humans checking recommendations and providing feedback to improve models.
AI with human approval
- Description: AI operates autonomously but requires human approval before execution.
- Example: Recommendation to change suppliers in a supply chain with supporting reasons.
Conditional autonomy
- Description: AI operates autonomously in normal conditions, routing to humans in the case of anomalies or unexpected situations.
- Example: Responding to customer inquiries, with unclear situations or customer sentiment triggers directed to humans.
AI with exceptions
- Description: AI makes decisions within its defined scope of capability, directing those that fall outside to humans.
- Example: Managing accounts receivable, directing any overdue payments or disputes to humans.
AI with oversight
- Description: AI operates autonomously in decision-making, but humans monitor the process and outcomes for compliance.
- Example: AI for inventory management and automated ordering, with regular human review and adjustment.
Full AI delegation
- Description: AI has complete autonomy in decision-making without human intervention, trusted in all scenarios.
- Example: AI autonomously managing and optimizing traffic flow.