In the ‘AI-Augmented Thinking & Decision-Making’ courses I was running last year I shared this framework of the elements and meta-patterns of Humans + AI thinking.
This is intended to be a starting point, providing simple examples of possible meta-patterns, which inspire people to discover and develop their own patterns.
A significant part of the value is in the idea itself of meta-patterns, so people can find ones that are useful and can be applied – with adaptation – across situations.
A detailed explanation is below the diagram
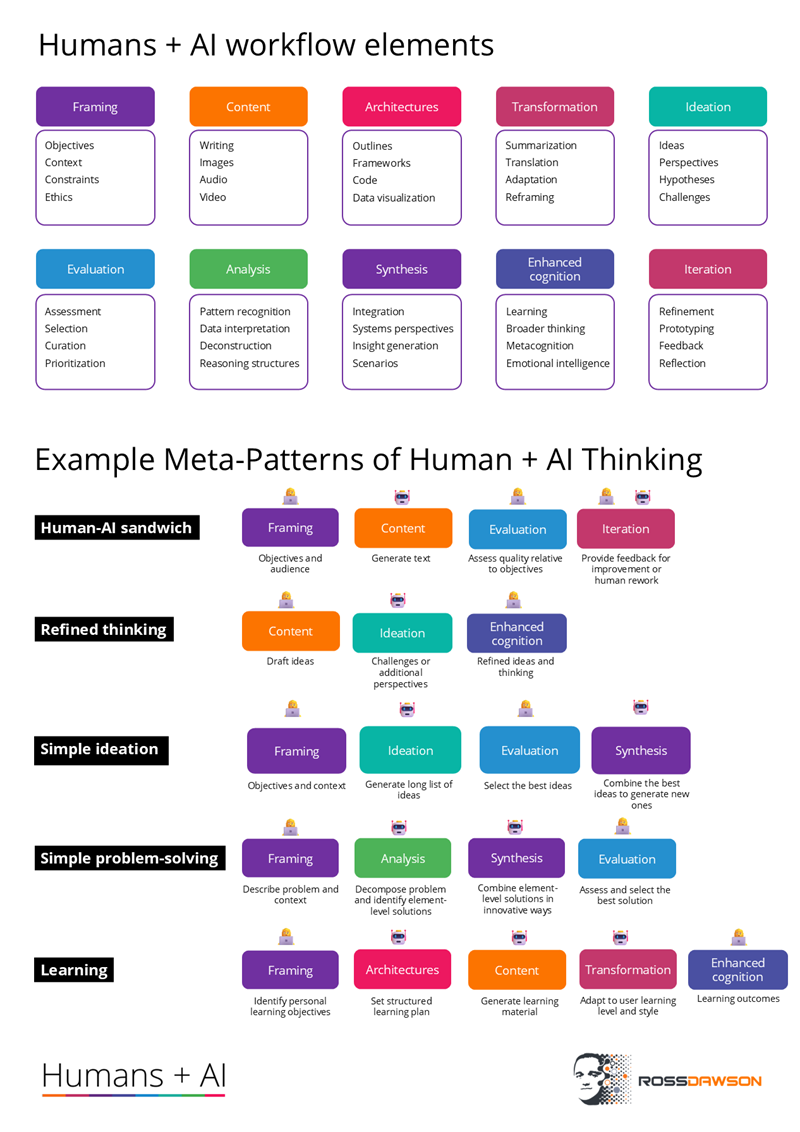
🔧 Core Elements of Humans + AI Thinking
These elements describe the types of cognitive and creative tasks that can be shared between humans and AI:
1. Framing
-
Human Role: Define goals, context, constraints, audience, and success criteria.
-
AI Role: Help clarify objectives, ask guiding questions, translate goals into structured inputs.
2. Content Generation
-
AI Role: Produce drafts, suggestions, or options for text, code, visuals, or plans.
-
Human Role: Evaluate, select, and refine outputs.
3. Architecting
-
Human Role: Conceptualize structures or frameworks (e.g., outlines, blueprints).
-
AI Role: Propose or elaborate on frameworks (e.g., article outlines, strategic models).
4. Transformation
-
AI Role: Summarize, translate, rephrase, adapt for new contexts.
-
Human Role: Specify format/audience and assess quality of transformation.
5. Ideation
-
AI Role: Rapidly generate ideas across broad domains or creative variations.
-
Human Role: Filter, adapt, and enhance those ideas.
6. Evaluation
-
AI Role: Score or compare alternatives using explicit criteria.
-
Human Role: Assess fitness for purpose and inject intuition/experience.
7. Analysis
-
AI Role: Discover patterns, perform data analysis, suggest correlations.
-
Human Role: Interpret meaning, validate relevance, bring nuance.
8. Synthesis
-
AI Role: Combine disparate insights into coherent narratives or summaries.
-
Human Role: Curate and verify integration, ensure logical flow.
9. Perspective Shifting
-
Human Role: Use AI to adopt alternate views (e.g., contrarian, customer, expert personas).
-
AI Role: Generate insights from unfamiliar angles.
10. Cognition & Reflection
-
Human Role: Think about your own thinking (metacognition).
-
AI Role: Prompt reflective questions, challenge assumptions, and help structure thinking.
11. Iteration
-
AI Role: Rapidly revise and refine outputs.
-
Human Role: Guide refinement with new feedback, explore trade-offs, prototype improved versions.
🔁 Key Metapatterns of Humans + AI Collaboration
These metapatterns describe the interaction dynamics between human and AI roles across tasks:
🥪 1. The Human–AI Sandwich
-
Human sets task → AI generates output → Human reviews and improves.
-
Simple but powerful iterative loop.
-
Used for writing, planning, coding, design, etc.
🧠 2. Human First, AI as Contrarian
-
Human creates ideas or direction → AI critiques, challenges, or provides alternate perspectives.
-
Enhances creativity, avoids blind spots.
💡 3. AI First, Human Refines
-
AI generates options or insight → Human selects and adapts.
-
Common in idea generation, document drafting, prototyping.
🌲 4. Chain of Thought (CoT)
-
Break down tasks into sequential reasoning steps.
-
Human or AI prompts the sequence; each step builds on the last.
-
Improves quality and structure of outcomes.
🌳 5. Tree of Thought / Branching Exploration
-
AI (or human) generates multiple possible directions.
-
Evaluate branches, then refine or combine best paths.
-
Encourages divergent and convergent thinking.
♻️ 6. Feedback Loops
-
Human evaluates → AI incorporates feedback → human re-evaluates → and so on.
-
Essential for improving quality over iterations.
🧠+🧠 7. AI as Thinking Partner
-
Dialogic process where AI acts like a peer: brainstorming, coaching, sounding board.
-
Used to push thinking beyond comfort zones.
🧭 Guiding Principles
-
Start with the Outcome: Always begin by clarifying what the human wants to achieve.
-
Metacognition is Central: Think about how you’re thinking—then use AI to improve it.
-
Leverage Complementarity: Know what humans do best (intuition, judgment, framing) and what AI does best (scale, speed, structure).
-
Keep Humans in the Loop: Avoid over-reliance—always include human oversight.
-
Prompt Iteratively: Good prompting is a process, not a one-shot command.




