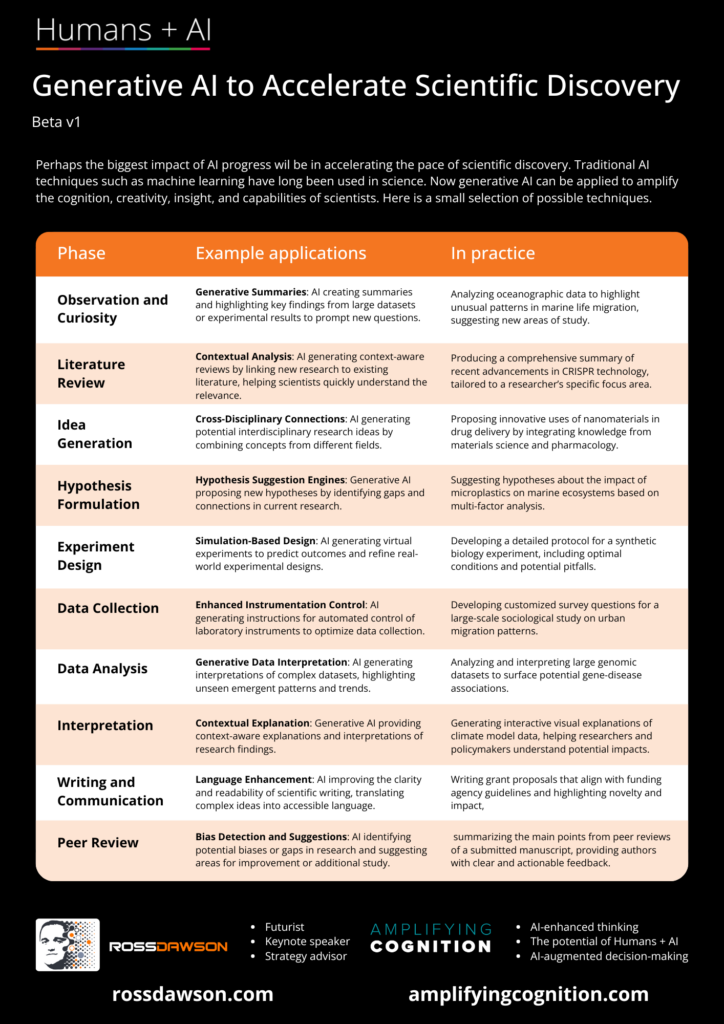
A map of GenAI to accelerate scientific discovery.
Click on the image for the full size pdf.
Generative AI to Accelerate Scientific Discovery
Phase
Observation and Curiosity
- Generative Summaries: AI creating summaries and highlighting key findings from large datasets or experimental results to prompt new questions.
- Example: Analyzing oceanographic data to highlight unusual patterns in marine life migration, suggesting new areas of study.
Literature Review
- Contextual Analysis: AI generating context-aware reviews by linking new research to existing literature, helping scientists quickly understand relevance.
- Example: Producing a comprehensive summary of recent advancements in CRISPR technology, tailored to a researcher’s specific focus area.
Idea Generation
- Cross-Disciplinary Connections: AI generating potential interdisciplinary research ideas by combining concepts from different fields.
- Example: Proposing innovative uses of nanomaterials in drug delivery by integrating knowledge from materials science and pharmacology.
Hypothesis Formulation
- Hypothesis Suggestion Engines: Generative AI proposing new hypotheses by identifying gaps and connections in current research.
- Example: Suggesting hypotheses about the impact of microplastics on marine ecosystems based on multi-factor analysis.
Experiment Design
- Simulation-Based Design: AI generating virtual experiments to predict outcomes and refine real-world experimental designs.
- Example: Developing a detailed protocol for a synthetic biology experiment, including optimal conditions and potential pitfalls.
Data Collection
- Enhanced Instrumentation Control: AI generating instructions for automated control of laboratory instruments to optimize data collection.
- Example: Developing customized survey questions for a large-scale sociological study on urban migration patterns.
Data Analysis
- Generative Data Interpretation: AI generating interpretations of complex datasets, highlighting unseen emergent patterns and trends.
- Example: Analyzing and interpreting large genomic datasets to surface potential gene-disease associations.
Interpretation
- Contextual Explanation: Generative AI providing context-aware explanations and interpretations of research findings.
- Example: Generating interactive visual explanations of climate model data, helping researchers and policymakers understand potential impacts.
Writing and Communication
- Language Enhancement: AI improving the clarity and readability of scientific writing, translating complex ideas into accessible language.
- Example: Writing grant proposals that align with funding agency guidelines and highlighting novelty and impact.
Peer Review
- Bias Detection and Suggestions: AI identifying potential biases or gaps in research and suggesting areas for improvement or additional study.
- Example: Summarizing the main points from peer reviews of a submitted manuscript, providing authors with clear and actionable feedback.